With everything being super-connected these days, it's important to communicate effectively in different languages—whether you're running a business, part of an organization, or just a regular person like you and I.
With the world getting all tangled up in connections, we're finding ourselves needing translations that aren't just accurate but also get the cultural vibes right.
Language is constantly evolving which makes things a little tricky.
Take for example new words like cakeage (an extra fee to bring your cake from outside the restaurant) and the Dutch word twerken from the English twerking 🍑
With language constantly evolving, keeping up is tough, especially if you're not multilingual. How are you supposed to support multiple languages inside your Knowledge Base?
Usually you outsource it.
And we're not just talking about totally different languages here—it may be regional differences you're targeting, like American English vs. British English or Latin American Spanish vs. Spanish (Castilian).
Two major players for outsourcing your multilingual Knowledge Base are machine translation and good ol' manual translation.
Both have their cool sides and not-so-cool sides, leading to this ongoing debate on which one is the real MVP for creating content in lots of different languages.
In this blog, we're diving into the nitty-gritty of both methods.
We'll break down what makes them awesome and what might make you go "hmm."
The goal? To help you figure out which translation method is the perfect match for your Knowledge Base.
So buckle up—we're about to get into it!
Definition and Differences
First things first—let's understand the difference between machine translation and manual translation so we're on the same page.
What's Machine Translation?
Machine translation refers to the use of computer algorithms to automatically translate text or speech from one language to another.
These algorithms analyze large datasets to learn patterns and linguistic structures, enabling them to produce translations quickly. Common examples of machine translation include tools like Google Translate and Microsoft Translator.
We provide our very own Machine Translations feature that allows customers to translate their default language into many others.
What's Manual Translation?
Manual translation on the other hand, involves the expertise of human translators who possess language proficiency and cultural understanding.
These professionals meticulously translate content, ensuring accuracy, nuance, and cultural sensitivity. For example, in British English you may say:
Running around like a headless chicken
whereas in American English you may say:
Running around like a chicken with its head cut off
Which may matter in context, although I must admit if you're using the above example in your Knowledge Base article I gotta wonder 💭
Manual translation encompasses a wide range of materials, from legal documents and technical manuals to creative works like literature and marketing content.
Differences Between Machine Translation and Manual Translation
Machine translations—the tech-savvy language wizards—use algorithms and machine learning (ML) technology to transform languages.
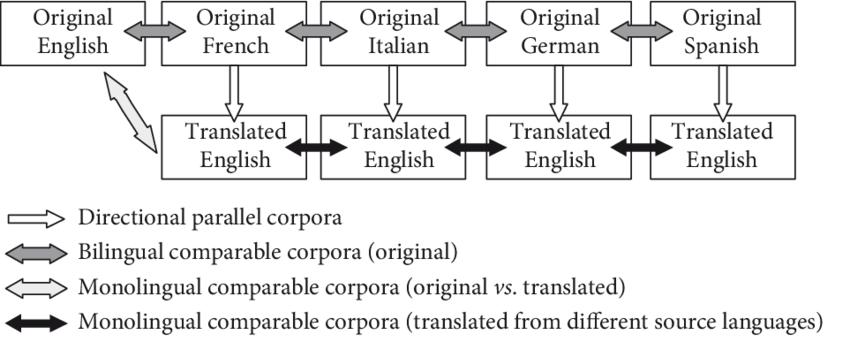
Interestingly to start with Google Translate simply utilized the Europarl Corpus, a bunch of documents from the European Parliament that were translated manually into 21 languages to start with.
Now the Corpus is part of a wider statistical machine translation algorithm that automatically translates European documents.
Anyhow, I digress. Machine translations can vary depending on the system their based on.
Google Translate now uses their neural machine translation technology (GNMT) to generate translations that include different idioms, forms, and tenses.
Microsoft have their Microsoft Translator service that uses their Azure AI technology to translate.
Apple has their own Translation app that uses their Natural Language framework.
Basically, Machine Translation uses a lot of data to work out how a sentence would change into a different language. They aren't 100% accurate and many translations may need to be manually reviewed for quality.
Now, on the flip side, we've got manual translations, where real-life human translators take the stage.
These language maestros bring not just their smarts but also their personal touch.
Unlike the quick and automated moves of machines, manual translators use their brains and experience to delicately translate content. It's all about getting it spot-on—accurate, nuanced, and culturally on point. They want that translation to vibe authentically with the folks they're talking to.
So, here's the deal: machine translations are like the speed racers, zipping through content with efficiency. But, hold up, they might stumble a bit with the subtle stuff—keeping the nuance, handling tricky content, and making sure it's culturally spot-on can be a bit tricky.
Now enter manual translations, powered by human intuition and a deep sense of culture. They're the navigators, gracefully gliding through the complexities but, fair warning, they take a bit more time and might ask for a bit more cash.
In a nutshell, choosing between machine and manual translations is like picking the right tool for the job.
What's your content like? What's your budget? And how picky are you about precision? It's all in the mix.
Benefits of Machine Translation
Let's explore the advantages that make machine translation a compelling choice when it comes to maintaining a multilingual Knowledge Base.
⚡ Need for Speed
One of the most significant advantages of machine translation is its speed.
Automated algorithms can process and translate vast amounts of content in a fraction of the time it would take a human translator. This rapid turnaround is especially valuable for businesses that need quick translations for time-sensitive information.
💰 Cost-Effectiveness
Machine translation can be more cost-effective, particularly for large volumes of content. Automated systems don't require salaries, benefits, or breaks, making them an economical option for organizations with budget constraints.
🥤 Handling Large Volumes of Content
Machine translation excels in handling large volumes of content efficiently.
Whether it's website localization, product descriptions, or user manuals, automated systems can quickly translate extensive datasets without compromising on speed.
Drawbacks of Machine Translation
Now, let's take a closer look at the other side of the coin.
While machine translation dazzles with its speed and efficiency, it's not all sunshine and rainbows. In this section, we'll uncover the drawbacks that come hand-in-hand with relying on automated systems.
🚮 Potential for Errors
One of the significant drawbacks of machine translation is the potential for errors.
Automated systems may misinterpret idioms, context, or subtle nuances, leading to inaccuracies in the translated content. This can be especially problematic in technical, legal, or creative materials where precision is paramount.
A study in 2016 showed that Neural Machine Translation (NMT) performed better overall than the older phrase-based (PBMT) technology, but shared that there was still potential for errors and still needed further work:
"...some aspects of NMT that deserve further work, such as the handling of long sentences and the reordering of particular linguistic constituents requiring a deep semantic understanding of text. Machine translation is definitely not a solved problem, but the time is finally ripe to tackle its most intricate aspects"
🤥 Lack of Nuance
Machines lack the innate understanding of cultural nuances and context that human translators possess. As a result, machine-translated content may lack the subtleties and cultural sensitivity required for effective communication.
Like I said earlier, language is ever-evolving and complex in its nature. Will your machine translations take this into account?
😵💫 Inability to Handle Complex Content
Machine translation struggles with the translation of highly specialized or complex content. Technical jargon, industry-specific terminology, and intricate details may be inaccurately translated, compromising the integrity and comprehensibility of the information.
Benefits of Manual Translation
Let's dive into the unique strengths and advantages that human expertise brings to the table.
🧠 Accuracy
Human translators bring a level of accuracy and precision that machines often struggle to achieve. Professionals with language expertise ensure that the translated content accurately reflects the intended meaning, maintaining the integrity of the original message.
🔁 Ability to Handle Complex Content
Manual translation is particularly valuable for content that requires a deep understanding of specialized fields.
Whether it's legal documents, medical texts, or technical manuals, human translators can navigate complex terminology and maintain the intended meaning.
🧶 Cultural Sensitivity
Humans possess cultural awareness and sensitivity, allowing them to adapt content to resonate with diverse audiences.
Manual translation ensures that cultural nuances are preserved, preventing potential misunderstandings or misinterpretations.
Drawbacks of Manual Translation
It's essential to acknowledge the challenges and pitfalls that accompany the human touch in translation. In this section, we'll uncover the drawbacks inherent in manual translation.
⏰ Time-Consuming
One of the primary drawbacks of manual translation is the time it takes to produce accurate translations. Human translators need adequate time to understand the context, conduct research if necessary, and carefully craft translations that capture the nuances of the source language.
💳 Higher Cost
Manual translation often comes with a higher cost compared to machine translation. Human expertise, time investment, and the need for quality assurance contribute to the overall expense.
However, this cost is justified by the accuracy and quality of the final product.
🧩 Potential for Human Error
While human translators strive for perfection, they are not immune to errors.
Typos, misinterpretations, or oversights can occur, emphasizing the importance of thorough proofreading and quality control processes.
Factors to Consider When Deciding Between Machine and Manual Translation
Choosing between machine and manual translation isn't a one-size-fits-all affair.
From the type of content and budget considerations to your precision requirements, these elements play a pivotal role in determining the most suitable translation method.

Our content in monthly bitesized emails
Get our best content delivered straight to your inbox.
SubscribeWith the rise of Knowledge Base AI assistants, particularly in the machine translation domain, adding a tech-savvy layer to the decision-making process in this dynamic linguistic landscape can solve but also cause problems.
In this section, we're unraveling the factors that should guide your choice.
Budget
Consider your budget constraints. If you have a limited budget and need to translate a large volume of content quickly, machine translation may be a suitable option. However, if quality is paramount and budget permits, manual translation may be more appropriate.
Content Type
The nature of the content plays a crucial role in the decision-making process.
Highly specialized, creative, or culturally sensitive content may benefit more from manual translation, while routine and straightforward information might be suitable for machine translation.
Target Audience
Understanding your target audience is essential. If your audience values cultural nuances and precise communication, manual translation may be the better choice.
For a broad audience with varied language proficiency, machine translation may suffice.
Best Practices for Machine and Manual Translation
In this section, let's dive into the best practices that can elevate your translation game, whether you're riding the automated wave of machine translation or savoring the nuanced touch of manual translation.
Use a Combination
In many cases, a hybrid approach combining both machine and manual translation can be effective. Use machine translation for initial drafts and then have human translators review and refine the content to ensure accuracy and cultural appropriateness.
Ensure Quality Control
Implement robust quality control processes regardless of the chosen translation method. Proofreading, editing, and feedback loops are essential to catch errors and refine the final product.
Use a Glossary or Style Guide
Maintain a glossary/style guide of terms specific to your industry or organization.

This ensures consistency across translations and reduces the risk of misunderstandings. Both machine and manual translators can benefit from a well-maintained glossary.
Create a Hybrid Translation Strategy for the Best End Results
Your Knowledge Base is like a treasure trove of wisdom, insights, and valuable information. And guess what? People worldwide are hungry for that knowledge.
So should you go all-in with machines or stick to the classic human touch?
Well, my friends, the sweet spot lies in the blend.
Using both machine and manual translations is like having the best of both worlds.
It's the Avengers of translation strategies, where each superhero brings something unique to the table.
The machines handle the heavy lifting—quick, efficient, and perfect for massive content loads. Then, our human heroes step in, ensuring accuracy, nuance, and that unbeatable cultural sensitivity.
